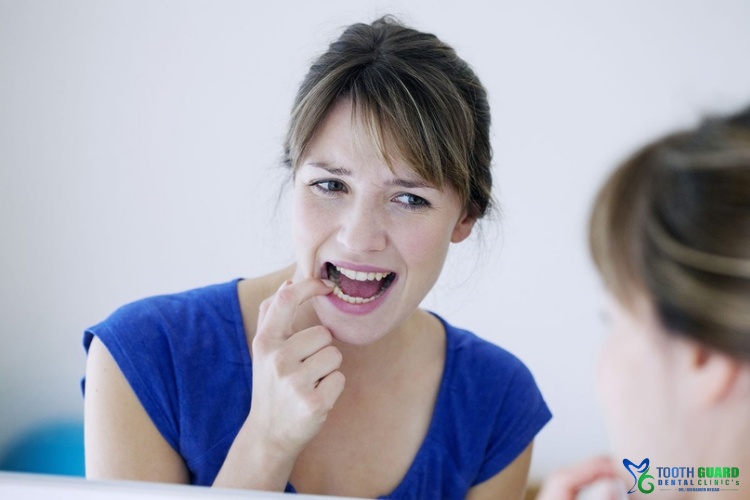

Gingivitis is one of the most prominent problems of the gums and teeth, as it causes irritation, redness, and swelling of the gums. This inflammation is often caused by the buildup of plaque or bacteria on the teeth.
Gingivitis is considered a non-destructive type of gum disease, but it requires quick treatment to avoid worsening the problem.
But not treating it can lead to the patient developing periodontitis, which is more serious and can ultimately lead to tooth loss.
Dr. Mohamed Hegab is considered one of the most famous dentists in Egypt for treating gingivitis, as he has modern devices and techniques used in treating dental problems.
Through the following lines, we will learn together about the types of gingivitis, and how long the treatment takes to heal from gingivitis.
It is the main cause of gingivitis Accumulating Food residue and bacteria on the surface of the teeth and in the spaces between the teeth, as this will lead to the formation of plaque, which is a thin layer of bacteria that appears on the surface of the teeth. The plaque layer can also harden to form what is called the tartar layer.
Continuous buildup of plaque and tartar can lead to infection in the gums, stimulating the immune system in the area. This immune response contributes to inflammation, causing swelling and redness in the gums.
Gingivitis can occur to any group of individuals, but there are some factors and reasons that make a number of individuals more susceptible to developing gingivitis, These reasons are as follows:
Lack of attention to oral and dental hygiene, which can make the gums more susceptible to sensitivity and inflammation.
Hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy, adolescence, and menopause.
The random growth of teeth and the presence of crooked teeth can lead to difficulty in cleaning the teeth well, which increases the risk of plaque and tartar accumulation and thus increases the possibility of gingivitis.
Smoking.
Some types of medications, such as:
Anticonvulsant medications.
Pills.
Steroids.
Calcium channel blockers.
Chemotherapy.
Angina medications.
Some diseases and health problems, including:
diabetes.
Immunodeficiency diseases such as HIV and AIDS increase the risk of gum disease due to the body's weak ability to fight infection.
Tumors and cancerous diseases.
Inappropriately sized dentures and dentures.
Malnutrition and deficiency of some nutrients, such as: vitamin C, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and vitamin A.
Getting older.
Genetic or genetic factors and a history of gingivitis in the family may increase the likelihood of developing gingivitis.
Tension and stress.
Gingivitis can be painful and you may want to know more about it. What you should know is that there are many forms of gingivitis, and the most important types of gingivitis are:
Gingivitis caused by fungi
Infection with a type of fungus called... By radiology Actinomyces gingivitis. This type of inflammation is characterized by the presence of a swollen area and the discharge of pus or abscess.
The disease also tends to form sinusoidal channels that connect With whipping It secretes purulent secretions containing sulfur granules due to its yellow appearance.
Hormonal gingivitis
High hormones such as estrogen and progesterone increase the sensitivity of the gums and make them more susceptible to plaque and bacteria, leading to inflammation, swelling, and bleeding that, if left untreated, may lead to bone and tooth loss.
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
Acute necrotizing ulcerative ulcerative gingivitis is a painful inflammation of the gums. Its symptoms are severe pain, bleeding, and bad breath. The diagnosis is based on clinical examination, and it occurs frequently in smokers and patients with weak immune systems who suffer from stress.
Gingivitis caused by diabetes
Gingivitis caused by diabetes. Reduced blood flow can weaken the gums and bones. This puts them at greater risk of infection, increasing the possibility of developing gingivitis, which is accompanied by redness, pain, swelling, and sometimes bleeding.
Gingivitis caused by caries
Sticky bacterial decay (plaque) that accumulates on the teeth may cause gingivitis, characterized by swelling and bleeding of the gums. This may lead to health problems beyond the teeth, such as serious diseases and complications, including heart attacks.
Periodontitis
It is the advanced stage of gingivitis, where the infection reaches the bones, leading to damage and tooth loss.
The duration of treatment for gingivitis depends on the type of inflammation and the severity of the condition. In many cases, the symptoms of gingivitis can disappear within 7-14 days when receiving appropriate treatment.
Many people suffer from swollen gums around the molars, with a group of accompanying symptoms. Let us learn about the causes and methods of prevention and treatment.
Swollen gums around the molar can occur for many reasons, such as poor dental hygiene and gum disease, and the condition may develop into gingivitis if the inflammation is not treated. The gumsWhich affects the tissues supporting the teeth and leads to their damage, in addition to damage to the jaw bone.
Factors causing swollen gums around the tooth include the following:
Smoking.
Diabetes.
AIDS.
Stress.
Genetic factors.
Crooked teeth.
Dental fillings.
Medicines that cause dry mouth.
Treatment of gingivitis Change the molar by doing the following:
Teeth cleaning: Plaque and bacteria are removed from tooth surfaces and under the gums while smoothing tooth roots, reducing tartar and bacteria buildup and speeding up the healing process.
Dental restoration: If necessary, as ill-fitting dental restorations may irritate the gums and prevent effective plaque removal.
Antibiotics: Oral antibiotics are often effective in treating tooth abscesses.
Root canal:It is a dental procedure that involves removing bacteria from the roots of infected teeth, and is known as root canal treatment.
Tooth extraction: Your dentist may need to remove the affected tooth, and this procedure requires local anesthesia.
Continuing care: And be sure to visit the dentist.
The severity of gingivitis symptoms varies between cases. In mild cases, patients may not notice any symptoms, while others may suffer from symptoms ranging from slight redness in the gums to pain and tooth loss, which leads to the need to treat gingivitis.
Below are the symptoms of gingivitis:
Gum redness.
Swollen gums.
Gum bleeding while brushing or flossing.
Bad breath.
As the disease progresses, the patient may exhibit the following symptoms:
Pain in the gums or teeth, especially while chewing food.
The appearance of an abscess in the area between the gums and teeth.
Gum recession.
Teeth loosening and falling out.
Changes in your bite, making your teeth appear mismatched.
An infection in the dental area that may spread to other parts of the body.
Read about dental filling cost
There is no quick-acting treatment for gingivitis, and there is no known best treatment for gingivitis The gumsAs each case requires a different medication from the other, the dentist may use several gingivitis medications that are used to complete the treatment stages, including the following:
Treatment of gingivitis With antibiotics
The most prominent and effective medications used to treat gum and tooth inflammation are the following:
Penicillin: Penicillin is considered one of the best antibiotics to treat acute Treatment of gingivitis , for patients who do not suffer from an allergy to it.
Erythromycin: Penicillin is considered one of the best antibiotics to treat acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, for patients who do not suffer from allergies to it.
Minocycline: Minocycline is used as a drug to treat gingivitis, and it is also an adjunct to dental cleanings and root canal removal, in addition to planning to reduce the depth of caries in patients suffering from gingivitis.
Doxycycline: Doxycycline is one of the best treatments for inflamed gums accompanied by periodontitis in adults as it helps prevent the growth of bacteria in the mouth.
There are different forms of antibiotics that the dentist prescribes to the patient to help treat the infection The gums They are the following:
Medical rinse to treat gingivitis: Medical mouthwash helps treat gingivitis by containing antibacterial components. Slow-degrading antiseptic wafers or pellets can be used, as the dentist places them in the gum pockets. To divorce The antibiotic should be administered slowly, which will reduce the size of the pocket and eliminate bacteria. A mouthwash containing chlorhexidine or metronidazole may also be used to promote healing.
Antibiotic gel: Gel or ointment can be used to treat inflammation The gums The antibiotic gel is placed on the gum pockets after deep cleaning to help control the infection.
Oral antibiotics: In cases of severe gingivitis, an antibiotic is taken in the form of capsules or pills orally.
Treatment of gingivitis With surgery
If all other treatment methods fail, the dentist resorts to surgery to treat advanced cases of gingivitis. Surgery options include the following:
Gum graft surgery: In gum graft surgery, the surgeon takes tissue from another part of the body, such as the palate, and implants it in the inflamed area of the gums to cover exposed parts of the teeth and prevent bone and tooth loss or decay.
surgery Flap: The surgeon lifts the gums to reach the depth of the tartar below the gum line, then sews it back into place so that the gum tissue is well wrapped around the tooth, preventing the buildup of tartar and plaque.
Finally, treating gingivitis is an essential step in maintaining oral and dental health, as it requires adherence to daily hygiene and visiting the doctor regularly to obtain the appropriate diagnosis and treatment. By following preventive and treatment guidelines, you can reduce the aggravation of the problem and ensure a long-lasting, healthy smile. You can contact us at tooth guard On +201555004694 for further inquiries.
You can learn more about dental nerve filling
اكتشف أحدث النصائح والمعلومات حول صحة الأسنان من خلال مدونتنا



Our team is ready to help with dates, answer your questions and guide you towards achieving your perfect smile